Understanding Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, affects the structures supporting your teeth. It includes your gums, soft tissues in your mouth, and the bones holding your teeth. The mildest form of gum disease is gingivitis, characterized by gum inflammation and redness.
When you have gingivitis, your gums may bleed easily when you brush your teeth. Fortunately, you can reverse this condition by maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental checkups. The end result may be that you suffer no tooth loss from periodontal disease.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease.

According to the American Dental Association, Receding Gums and Periodontal Disease May Be Related to Hereditary Factors
In periodontitis, the tissues and bone supporting your teeth become damaged, leading to receding gums and loosening teeth. Eventually, tooth loss can occur. RThis can occur with chronic periodontitis- slow general bone loss, or aggressive periodontitis- acute infection around one or two teeth. Symptoms of periodontal disease include swollen, tender gums, bad breath, and loose teeth. Having loose teeth can have the effective of noticeably changing your bite.
To maintain healthy gums, brush and floss your teeth daily. Regular dental checkups also play a vital role in detecting and treating gum disease before it worsens. Keep in mind that while genetics may influence your susceptibility to periodontal disease, environmental factors like smoking and diabetes have an even larger impact.
Remember, taking care of your oral health is crucial in preventing periodontal disease and maintaining a confident, healthy smile.
Identifying Risk Factors of Periodontal Disease
To understand if periodontal disease is hereditary, you should first know the key risk factors. Many common diseases, including periodontal disease, result from gene-environment interactions. However, no gene has had as large an impact as environmental factors like smoking and diabetes.
You can group risk factors for periodontitis into two main categories: lifestyle and genetics. By focusing on these common causes, you can help prevent or manage the condition.
Lifestyle Factors:
- Poor oral hygiene: Skipping regular brushing and flossing allows plaque to build up and harden, leading to gum infections as well as tooth decay.
- Tobacco use: Smoking harms gum tissue, reduces the effectiveness of your immune system, and is a significant factor that boosts your risk of periodontal disease.
- Bad breath: Persistent bad breath may be a sign of bacteria growth and poor oral health.
Genetic Factors: Research suggests that genetic risk factors may contribute to the onset of gingivitis and eventually periodontitis. However, specific risk factors remain difficult to identify due to the complex interplay among genetics, environment, and personal habits.
Preventing periodontal disease involves maintaining good oral hygiene and avoiding harmful lifestyle factors. Keep in mind bleeding gums and loose teeth are common symptoms of periodontitis. If you experience these symptoms, visit a dental professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.

Research Seems to Suggest That Periodontal Disease May Have a Hereditary Component
Evidence of Heredity in Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease results from a complex interplay between genes, bacteria, and environmental factors. Research shows that your genetics play a significant role in your susceptibility to this condition. To understand the genetic aspect, let’s examine key terms and concepts.
Your body consists of millions of cells, and within each cell, there are chromosomes that carry genes. Genes determine traits and characteristics, and when discrepancies occur, they may result in diseases, including periodontal issues. Genotype refers to your exact genetic makeup, while phenotype denotes the physical and observable traits.
Autosomal recessive inheritance occurs when both parents pass on a gene mutation, increasing the risk of developing specific conditions. Understanding this link helps you identify potential genetic factors influencing your oral health.
In the case of periodontal disease, studies reveal that up to a third of the variation in the population is due to genetic factors. This correlation gets stronger with disease severity. Proteins also play a crucial role in the process, as improper protein function can lead to inflammatory responses and increase the risk of periodontal disease.
Twin studies provide valuable insights into genetic influences. For example, if one twin has periodontal disease and their sibling – whether identical or not – also exhibits the condition, this supports a genetic component. While twin studies can’t definitively confirm a genetic cause, they offer essential clues to understanding the contribution of genetics to periodontal health.
In summary, your genetics, along with environmental factors, determine your susceptibility to periodontal disease. Knowing your genetic background and understanding key terms, such as phenotype and autosomal recessive inheritance, helps you grasp the hereditary aspect of this condition. Be mindful of these factors and practice good oral hygiene to maintain optimum periodontal health.
Diagnosing Periodontal Disease
When you suspect periodontal disease, visiting a dentist should be your priority. A dental exam is used to diagnose periodontal disease. During this exam, your mouth will be examined and checks will be made for warning signs like red, bleeding gums, or loose teeth. Don’t ignore these symptoms, as they might indicate a more severe form of gum disease: periodontitis.
To determine the severity of your condition, the dentist will review your medical history. They’ll look for factors that contribute to gum disease, such as medications and tobacco use. A professional dental cleaning helps remove plaque buildup and provides an accurate assessment of your oral health.
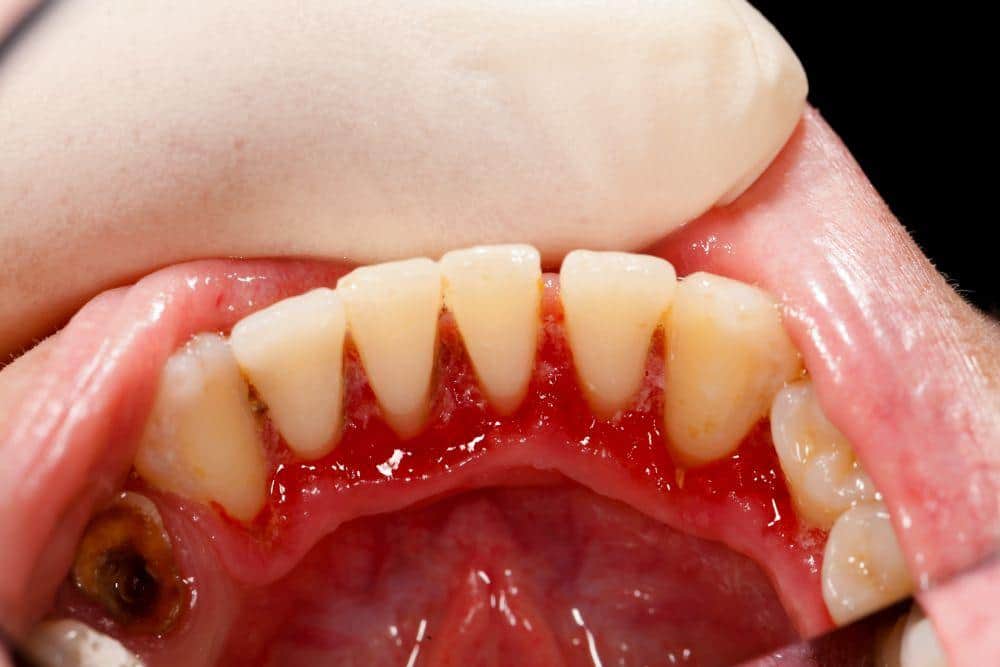
Periodontal Disease is Characterized by Red, Inflammed Gums
During your appointment, the dentist will use a small dental instrument called a probe to measure the depth of pockets around the base of your teeth. Healthy gums have shallow pockets, while deeper pockets and bleeding indicate gum inflammation or periodontal disease. This evaluation helps the dentist develop a personalized treatment plan for your needs.
Remember, early diagnosis of gum disease can prevent more significant oral health issues like tooth loss or worsening conditions like gingivitis. Maintain regular dental visits and practice proper oral hygiene to keep your teeth and gums in top shape.
Treatment And Management of Periodontal Disease
Maintaining your oral health is key in treating and managing periodontal disease. One important aspect is regular flossing to help prevent the buildup of plaque and bacteria. Visiting our dental office can also be beneficial for professional cleaning and guidance on proper oral care.
To manage periodontal disease, you need to address any existing pockets between your gums and teeth. Your periodontist can perform deep cleaning procedures to remove plaque and tartar below your gumline. This process helps reduce inflammation and the depth of pockets, which, in turn, aids in the prevention of gum recession and bone loss.
In some cases, more invasive treatments may be necessary to manage advanced periodontal disease. These might include gum or bone grafts to repair the damaged tissues, or dental appliances to balance your bite and protect your remaining teeth.
In conclusion, the management of periodontal disease revolves around good oral hygiene practices, regular professional cleanings, and appropriate treatments as advised by your periodontist. By adopting these measures, you can effectively control periodontal disease and maintain your oral health.
Periodontal Disease And Its Complications
You might not know that periodontal disease, also called gum disease, is a severe infection harming the soft tissue surrounding your teeth. This issue could lead to tooth loss and is fairly common in adults.
To understand the process, know that periodontal disease has various stages. It all starts with dental plaque forming on your teeth. If not removed, this plaque may harden and cause your gums to swell. This stage is called gingivitis. When left untreated, it advances to periodontitis, where gums pull away from teeth, creating pockets prone to infection. Gradually, it can damage the bone structures supporting your teeth, resulting in tooth loss.
Looking at the genetic aspect of gum disease, some individuals have a higher susceptibility due to their genetic makeup. While it’s not completely hereditary, certain genes might put you at risk. Also, factors like poor oral hygiene or smoking can trigger periodontal disease in those predisposed.
Keep in mind that periodontal disease might cause more complications, such as gum recession and weakened teeth support. Any teeth with root exposure are more susceptible to dental caries, or cavities. These issues can impact your overall oral health and even your general well-being.
In summary, be aware of your family history and take care of your oral hygiene to prevent periodontal disease and its complications. Always consult a dental professional for guidance and thorough check-ups.
The Role of Professional Oral Care
Your oral health plays a crucial role in preventing periodontal disease. A dentist or periodontist can provide personalized care to ensure your teeth and gums remain healthy. Regular check-ups are necessary, as they identify potential issues before they escalate.
During a dental visit, a professional cleaning takes place. Dental hygienists perform this routine procedure to remove plaque and tartar, decreasing the risk of gum inflammation and the onset of periodontal disease. They also offer essential advice for maintaining proper oral hygiene at home. Incorporate their recommendations into your daily routine to improve your oral health.
MedlinePlus suggests that individuals with a family history of periodontal disease might require extra precautions. If you’re at a higher risk, discuss your concerns with your dentist or periodontist. They can suggest advanced preventive measures, including specific oral care aids to combat the hereditary factors associated with gum disease.
Remember, professional oral care and diligent at-home practices are essential in maintaining optimal dental health and minimizing the risk of hereditary periodontal disease. You should see your dentist regularly, even if you aren’t experiencing any symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors contribute to the development of periodontal disease?
Several factors can contribute to developing periodontal disease, including poor oral hygiene, tobacco use, and certain medical conditions like diabetes. Additionally, medications can cause dry mouth, which can increase the risk of gum disease. Uncontrolled plaque buildup is a major contributor to periodontal disease.
Can genetic predisposition lead to gum disease?
Yes, genetics can play a role in the development of periodontal disease. However, no single gene has been identified as having a significant impact compared to environmental influences, such as smoking or diabetes. Still, a genetic predisposition can increase your risk, so you should maintain good oral hygiene to help minimize that risk.
How can one prevent hereditary periodontal disease?
To prevent hereditary periodontal disease, you should practice good oral hygiene, which includes regular brushing and flossing, as well as dental checkups. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding tobacco products, and managing underlying health conditions are also essential steps in preventing gum disease, even if you have a genetic predisposition.
Are certain age groups more susceptible to periodontal disease?
Periodontal disease can affect individuals of any age, but the risk increases with age. Adults over the age of 30 are at a higher risk, and the prevalence of periodontal disease continues to rise with each decade.

The Risk of Periodontal Disease Increases as we Age
What treatments are available for hereditary gum disease?
Treatments for hereditary gum disease are similar to those for non-hereditary gum disease, focusing on controlling the infection and preventing further damage. This may include scaling and root planing to remove plaque and tartar, medication to treat infection, and surgical treatments if the disease is advanced.
Is there a link between gingivitis and genetic factors?
Gingivitis, which is a milder form of gum disease, can be influenced by genetic factors as well. However, like with periodontal disease, environmental factors and lifestyle habits play a more significant role in the development of gingivitis. It’s crucial to maintain good oral hygiene to prevent gingivitis, even if you have a genetic predisposition.