Key Takeaway: Periodontal Disease Might be Somewhat Contagious
Periodontal Disease can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor oral hygiene. While transmission of harmful bacteria found in infected saliva may possibly contribute towards periodontal disease, it isn’t typically how periodontal disease occurs. Even if you somehow contract harmful bacteria from others, proper oral hygiene can usually be employed to prevent the formation of periodontal disease.
Is Periodontal Disease Contagious?
You might wonder if periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is contagious. Well, the answer is not as straightforward as it might seem. Periodontal disease results from a build-up of bad bacteria in the mouth, causing plaque and leading to inflammation of the gums and bone tissue supporting your teeth.
Keep in mind that bacteria can be exchanged through saliva, especially during close contact such as kissing or sharing eating utensils. In family settings, there’s an increased likelihood of spreading such bacteria among family members.

This Video From the American Dental Association Describes How A Periodontal Screening From a Dentist Like Dr. Murphy Can Identify Potential Periodontal Problems & Other Issues
However, you should remember that not everyone exposed to these bacteria will develop periodontal disease. The risk of developing the condition depends on several factors, including your oral hygiene habits, immune system, and genetics.
To avoid potential transmission and prevent periodontal disease, maintain good oral hygiene practices. Brush your teeth at least twice a day, floss daily, and visit Dr. Murphy regularly for check-ups and dental cleanings.
In summary, while periodontal disease might not be directly contagious like a cold or flu, the exchange of bacteria through saliva and close contact can increase the risk of developing the condition. Your best defense is maintaining a healthy oral hygiene routine and being mindful of sharing saliva in close-contact situations.
Understanding Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, also called gum disease, is a common issue that affects the tissues around your teeth. It starts as gingivitis, which is the early stage of the disease. The main cause of this condition is poor oral hygiene causing a bacterium overload which makes plaque buildup . You can prevent periodontal disease by taking proper care of your oral health.
To better comprehend periodontal disease, you must know its symptoms. Some common signs include red, swollen gums, inflammation, and bleeding gums when brushing or flossing. Persistent bad breath is another indicator that you should pay attention to. Bad breath can have a few different causes, all of which need to be addressed.
Periodontal disease progresses to periodontitis if it stays untreated. During this stage, the inflammation becomes more severe, damaging the soft tissue and eventually the bone supporting your teeth. Consequently, your teeth may become loose or even fall out.
To avoid the onset of periodontal disease, you must improve your oral care routine. Brush your teeth daily, floss regularly, and come in to our office in Fort Collins for regular cleanings and dental exams. By following these steps, you can keep your gums healthy and protect your teeth from any possible damage.
Risk Factors and Causes

It May Seem Harmless, but Sharing a Tooth Brush is Never a Good Idea as It Allows for the Sharing of Potentially Harmful Bacteria
When it comes to your oral health, several factors might increase your risk of developing periodontal disease. One primary cause is the buildup of bacteria around your teeth. These bacteria form a sticky film called plaque, which can harden into tartar if not removed. Tartar can only be removed by a dental professional during cleanings. Poor oral hygiene can cause this buildup, so make sure to brush and floss regularly to keep your teeth and gums clean and healthy.
Several factors can increase your risk of developing periodontal disease. Smoking, for example, weakens your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off the bacteria in your mouth. This leads to a higher risk of infection and inflammation, causing your gums to suffer. If you smoke, consider quitting to improve your oral health and protect your gums.
Another risk factor is diabetes. If you have diabetes, you’re more prone to infections, including gum disease. High blood sugar levels can damage your blood vessels, making it difficult for your body to deliver essential nutrients to your gums and teeth. Keep your blood sugar levels under control to maintain a healthy mouth.
Hormonal changes in your body can also play a role. These hormonal shifts—typically seen in women during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause—can make your gums more sensitive and prone to infection. Regular dental check-ups can help catch any changes early on.
Your genetics might also put you at risk for periodontal disease. If gum disease runs in your family, you might have a higher likelihood of developing it yourself. Talk with Dr. Murphy about your family history to determine if you need more frequent dental treatments or preventive measures.
Medications, stress, and illness can also put your oral health at risk. Some medications cause dry mouth or gum swelling, making it easier for bacteria to thrive. Stress can weaken your immune system, reducing your body’s ability to fight off infections. Illnesses, especially those that affect your immune system, can also make you more susceptible to oral health problems. Maintain regular dental check-ups and share any concerns with Dr. Murphy to keep your gums and teeth healthy.
Prevention and Management
To prevent gum disease, maintain good oral hygiene. Be sure to brush your teeth twice daily. Replace toothbrushes every three to four months or when the bristles wear out.
Flossing daily can remove plaque and food debris from areas your toothbrush can’t reach. In addition, consider using a mouth rinse to help reduce plaque and bacteria. Keep in mind the importance of regular dental checkups and professional cleanings. With consistent daily care, you can protect your teeth and gums from infection and inflammation.
Schedule dental cleanings at least twice a year. At your cleanings the hygienist will remove the accumulation of tartar and plaque from your teeth. These appointments also allow Dr. Murphy to assess your oral care routine and offer recommendations for improvement.
In summary, follow these steps for effective prevention and management of periodontal disease:
- Brush your teeth twice a day
- Floss daily
- Use a mouth rinse
- Attend regular dental checkups and cleanings
- Ensure consistent daily oral care
Clinical Examination and Diagnosis
When you notice warning signs, it’s essential to call our office to set up a dental exam. Dr. Murphy will conduct a thorough examination to diagnose periodontal disease and determine its severity.
First, Dr. Murphy evaluates your teeth and gums visually. They look for signs of inflammation, bleeding, or gum recession. This step helps identify potential issues, but it’s just the beginning.
Frequent, Periodic Dental Exams Can Identify Periodontal Issues Before They Become Serious Problems
During the examination, Dr. Murphy measures the depth of pockets around your teeth using a tool called a periodontal probe. Deep pockets and bleeding often indicate periodontal disease. Taking x-rays also provides valuable information about bone loss, which is common in advanced cases. Gum and bone recession can expose root structure, which is more susceptible to tooth decay.
Dr. Murphy will also ask about your medical history because certain factors, like smoking or diabetes, can contribute to periodontal disease. This information helps Dr. Murphy to develop an appropriate treatment plan based on your requirements.
Throughout this process, communication is vital. Ensure you share any concerns or symptoms with your dental professional to receive the most accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Effect on General Health
When it comes to periodontal disease, your overall health can be affected in various ways. It’s essential to be aware of these potential impacts and take the necessary steps to protect your health.
One connection between periodontal disease and general health is an increased risk of heart disease. When bacteria from the infected gums enter your bloodstream, they can create inflammation in your blood vessels, which may contribute to the development of heart disease.
Another factor to consider is the relationship between periodontal disease and damage to your soft tissue and bone. The infection can weaken the support system that keeps your teeth in place, leading to bone loss. When this support is compromised, your teeth can become loose, ultimately causing tooth loss.
To maintain your overall health and lower these risks, it’s crucial to consult with a periodontist in addition to your general dentist. While your general dentist specializes in restorative dentistry, they specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of gum disease and can help you manage your condition more effectively.
In conclusion, periodontal disease can have a significant effect on your general health by increasing your risk of heart disease and causing damage to your soft tissue and bone that lead to tooth loss. It’s essential to work closely with a periodontist, who can help you take the necessary steps to protect your overall well-being.
Treatment Options
The good news is that periodontal disease can be effectively treated in most casese.
If you are dealing with periodontal disease, seeking help from a dentist is vital. They can recommend various treatments based on the severity of your gum infection. Here are some available options.
Scaling and root planing: Tartar and plaque are removed from your teeth and smoothing the root surfaces. It helps prevent further buildup and allows your gums to reattach to your teeth.
Antibiotics: Dr. Murphy may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics to control the bacterial infection responsible for periodontal disease.
Surgery: In severe cases of periodontal disease, surgical interventions such as flap surgery, bone grafting, or guided tissue regeneration might be necessary. These procedures aim to remove infected tissues, promote bone growth, and encourage the attachment of healthy gum tissue.
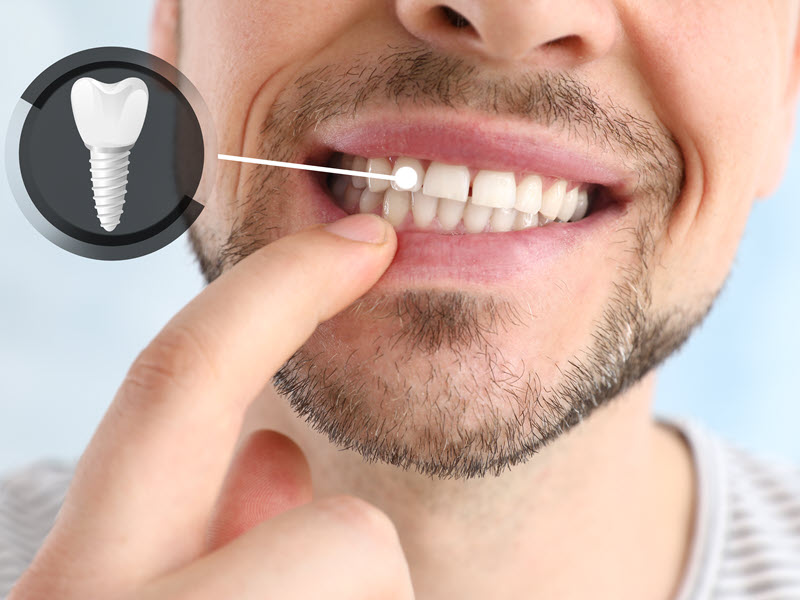
In the event that you have already experienced tooth loss, dental implants may become necessary. A dental implant is a long, lasting replacement for your natural tooth that looks, feels, and functions just like your missing tooth.
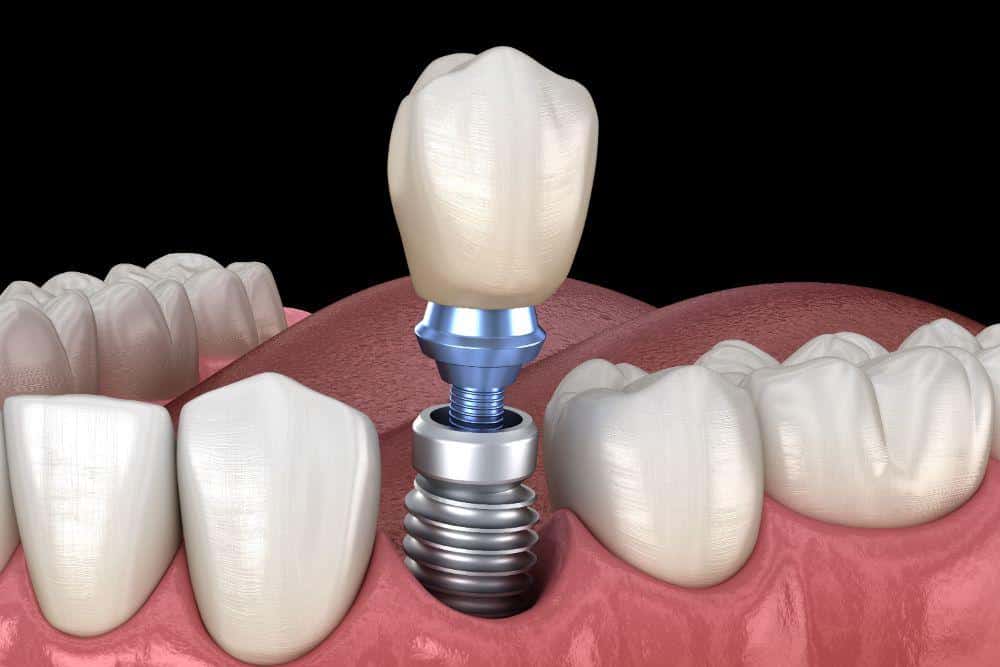
A Dental Implant is Used to Replace a Missing Tooth
Remember that maintaining good oral hygiene and undergoing regular dental checkups are crucial in preventing and managing periodontal disease effectively. So, take care of your teeth and gums by brushing, flossing, and visiting Dr. Murphy regularly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can periodontal disease spread through kissing?
While periodontal disease is primarily caused by poor oral hygiene, some studies suggest that bacteria responsible for gum disease can be transferred through saliva, such as during kissing. However, maintaining good oral care can significantly reduce your risk of developing periodontal disease.
Is it possible for periodontitis to be contagious between pets?
Yes, periodontal disease can be contagious between pets. Just like humans, pets can develop gum disease due to poor dental hygiene. Regular teeth cleaning and dental check-ups with a veterinarian are essential to keep your pet’s mouth healthy. Cats are particularly prone.
Can gum disease affect other parts of the body?
Gum disease can indeed affect other parts of your body. Research has shown links between periodontal disease and conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory diseases. It’s essential to maintain good oral hygiene and seek professional treatment if you suspect gum disease.
Is periodontal infection transferable?
Periodontal infection can be transferable through the exchange of oral bacteria. Common ways of transferring bacteria include sharing utensils, toothbrushes, or through saliva contact. To minimize the risk, practice good oral hygiene and avoid sharing items that come into contact with your mouth.
Is there a cure for periodontal disease?
There is no single “cure” for periodontal disease, but it can be managed through professional treatment and proper oral hygiene. Early stages like gingivitis can be reversed with improved dental care. In more severe cases, a periodontist may recommend treatments like scaling and root planing, or even surgery.
How quickly does gum disease progress?
The speed at which gum disease progresses varies depending on factors like your oral care routine, genetics, and overall health. Maintaining a consistent oral care routine and visiting Dr. Murphy regularly can help slow down or prevent the progression of gum disease.